Table of Contents
ToggleIndian Rupee Reaches All-Time Low of ₹90.25 Against US Dollar: Complete Market Analysis
The Indian Rupee (INR) has reached an all-time low of ₹90.25 against the US Dollar (USD) on December 3, 2025. Currently trading at ₹90.20 per dollar, the currency has depreciated 7.8% year-to-date, marking a significant milestone in India's currency history.
This analysis examines the factors behind this movement, its impact on various economic sectors, and the Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) response measures.
📊 Key Market Data (Dec 3, 2025)
| Current Exchange Rate | ₹90.20 / $1 |
| All-Time Low (Today) | ₹90.25 / $1 |
| YTD Depreciation | -7.8% ↓ |
| Forex Reserves (Nov) | $588 Billion |
| Trade Deficit (Oct) | $31.5 Billion |
| US Dollar Index | 107 points |
Market Context: The Rupee's movement comes amid the US Federal Reserve maintaining interest rates at 5.25-5.50% and foreign portfolio investors withdrawing ₹42,800 Crore from Indian markets in October-November 2025. Source: RBI, NSE
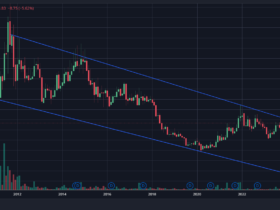
📈 INR/USD Historical Trend (2015-2025)
This chart shows the 10-year exchange rate movement between the Indian Rupee and US Dollar, highlighting the gradual depreciation trend.
🔍 Historical Observations
- 2015-2018: Relatively stable at ₹63-68 per dollar
- 2020: COVID-19 impact pushed rate to ₹74
- 2022-2023: Fed rate hikes accelerated depreciation to ₹83
- Dec 2025: Reached ₹90.25 due to strong dollar and trade deficit
🔍 Key Factors Behind the Rupee's Movement
The Rupee's depreciation to ₹90.20 is driven by multiple macroeconomic factors. Here's an analysis of the primary drivers.
1. 💵 Strong US Dollar (DXY at 107)
The US Dollar Index (DXY) reached 107 points in December 2025, driven by the Federal Reserve maintaining interest rates at 5.25-5.50%. This has increased global demand for dollar-denominated assets.
Historical Pattern: Typically, a 1% rise in DXY correlates with 0.3-0.5% depreciation in emerging market currencies including INR.
2. 📉 Trade Deficit at $31.5 Billion
India's trade deficit reached $31.5 billion in October 2025, influenced by crude oil prices at $95/barrel and increased gold imports during the festive season.
| Component | Oct 2025 |
|---|---|
| Crude Oil | $18.7B |
| Gold | $7.2B |
| Electronics | $9.8B |
| Exports | $38.9B |
3. 🌍 Foreign Portfolio Outflows: ₹42,800 Crore
Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) withdrew ₹42,800 Crore from Indian markets in October-November 2025, influenced by attractive US Treasury yields at 5.2%.
Note: FPI flows are a key driver of short-term currency movements in emerging markets. Source: NSDL, SEBI
4. 🏦 RBI's Forex Reserve Management
India's forex reserves declined from $645 billion (Sept 2024) to $588 billion (Nov 2025), a reduction of $57 billion. RBI has been actively managing reserves to maintain orderly market conditions.
The central bank balances currency stability objectives with the need to preserve adequate reserve buffers for future requirements.
📊 Impact on Indian Economy & Markets
The Rupee's depreciation to ₹90.20 has notable implications across various sectors of the Indian economy. Here's an analysis of how different segments are being affected.
Rising Inflation
Retail inflation reached 6.8% in November 2025. Import-dependent items like fuel, electronics, and certain medicines have seen price increases of 8-12%.
Foreign Expenses Higher
International travel and overseas education costs have increased by 7-10%. A $50,000 education now costs ₹45.1 Lakh compared to ₹42 Lakh last year.
Corporate Debt Pressure
Companies with foreign currency debt face 7.8% higher repayment costs. This particularly affects aviation and infrastructure sectors with significant dollar-denominated liabilities.
IT Sector Benefits
Export-focused IT companies are seeing improved margins of 4-5%. Major firms like TCS, Infosys, and Wipro benefit from dollar-denominated revenues.
NRI Remittances
NRIs receive ₹90.20 per dollar compared to ₹83.50 last year — an 8% increase. India's remittances are projected to reach $125 billion in 2025.
Export Competitiveness
Indian exports gain 7-8% price competitiveness globally. Textile, pharmaceutical, and chemical sectors are showing strong export growth trends.
📊 Sector-wise Performance Analysis (Dec 2025)
| Sector | Trend | Key Factor |
|---|---|---|
| IT Services | Positive ↑ | Dollar revenues boost margins 4-5% |
| Pharma | Positive ↑ | Export competitiveness improves |
| Aviation | Negative ↓ | Higher fuel costs impact margins |
| Oil Marketing | Negative ↓ | Crude at $95/barrel pressures margins |
| Automobiles | Mixed ± | Import costs up, exports benefit |
| Banking | Mixed ± | Forex gains offset by loan concerns |
Note: Currency movements affect different sectors differently based on their revenue sources and cost structures. Export-oriented sectors typically benefit from rupee depreciation, while import-dependent sectors face margin pressure. This analysis is for educational purposes only.
🏦 Reserve Bank of India's Response Measures
The Reserve Bank of India, under Governor Shaktikanta Das, has implemented several measures to manage currency volatility. Here's an overview of the key interventions.
🛡️ Key Intervention Measures
Forex Market Operations
RBI has utilized approximately $57 billion from forex reserves since September 2024 for market operations, bringing reserves to $588 billion as of November 2025.
Interest Rate Policy
The repo rate is maintained at 6.50%, balancing inflation management with growth objectives. The Monetary Policy Committee reviews this stance regularly.
Forward Market Management
Active management of forward premiums to reduce speculative activity and provide stability for businesses hedging currency exposure.
Rupee Internationalization
Promoting INR-denominated trade with 18 countries including Russia, UAE, and Bangladesh to reduce dollar dependency in bilateral trade.
⚡ Key Challenges
-
Global Dollar Strength:
The US Federal Reserve's policy stance continues to support dollar strength globally, affecting all emerging market currencies.
-
Structural Trade Balance:
India's import requirements, particularly crude oil, create ongoing dollar demand that requires careful management.
-
Policy Balance:
RBI must balance multiple objectives including currency stability, inflation control, and economic growth support.
⚠️ Important: This analysis is for educational and informational purposes only. It does not constitute investment advice or recommendations to buy, sell, or hold any securities. Market conditions are subject to change. Please consult a SEBI-registered financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the current INR/USD exchange rate?
As of December 3, 2025, the Indian Rupee is trading at ₹90.20 per US Dollar. It touched an all-time low of ₹90.25 earlier today, representing a 7.8% depreciation year-to-date.
2. What factors are driving the Rupee's movement?
Key factors include: (1) Strong US Dollar Index at 107 points due to Fed rates at 5.25-5.50%, (2) India's trade deficit of $31.5 billion in October, (3) FPI outflows of ₹42,800 Crore, and (4) Global crude oil prices at $95/barrel. Source: RBI, SEBI, NSE
3. How does this affect everyday Indians?
Retail inflation reached 6.8% in November 2025. Import-dependent items like electronics, fuel, and certain medicines are 8-12% costlier. Foreign education and travel costs have increased by 7-10%. However, NRIs benefit from better exchange rates when sending remittances to India.
4. Which sectors are affected positively?
Export-oriented sectors typically benefit from rupee depreciation. IT services companies see improved margins from dollar revenues. Pharmaceutical exporters gain pricing competitiveness. Textile and chemical sectors show strong export growth trends. This is an observation of market patterns, not a recommendation.
5. What is RBI doing about this?
RBI has utilized approximately $57 billion from forex reserves since September 2024 for market operations. The central bank maintains the repo rate at 6.50% and actively manages forward markets. RBI also promotes rupee internationalization through INR-denominated trade with 18 countries.
6. Will the Rupee strengthen soon?
Currency movements depend on multiple global and domestic factors including US Fed policy, crude oil prices, and India's trade balance. Market analysts suggest the rupee may trade in a range based on these evolving factors. Currency forecasting involves significant uncertainty.
7. How can I protect myself from currency fluctuations?
Currency risk management strategies vary based on individual circumstances. Some market participants use diversification, hedging instruments, or maintain exposure to export-oriented sectors. However, these decisions should be made after consulting a SEBI-registered financial advisor who can assess your specific situation.
8. Where can I track live exchange rates?
Live INR/USD rates are available on RBI's official website, NSE, BSE, and major financial platforms like Bloomberg, Reuters, and Moneycontrol. Banks also provide real-time forex rates on their websites and mobile apps.
⚠️ Disclaimer: This article is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute financial, investment, or trading advice. All data is sourced from RBI, SEBI, NSE, and other credible institutions as of December 3, 2025. Market conditions are subject to change. Please consult a SEBI-registered financial advisor before making any investment decisions. Past performance does not guarantee future results.







Leave a Reply